What is the Symbol of the Resistor?
I. Introduction
In the realm of electrical engineering, resistors play a pivotal role in controlling the flow of electric current within circuits. These components are essential for a variety of applications, from simple household devices to complex electronic systems. Understanding the symbol of the resistor is crucial for anyone involved in circuit design or analysis, as it serves as a universal language among engineers and technicians. This article aims to delve into the symbol of the resistor, its historical context, and its significance in circuit diagrams.
II. Understanding Resistors
Resistors are passive electrical components that limit the flow of electric current in a circuit. Their primary function is to provide resistance, which can be used to control voltage and current levels. Resistors come in various types, each serving specific purposes:
A. Basic Function of Resistors
1. **Limiting Current Flow**: Resistors are primarily used to limit the amount of current that can flow through a circuit. By introducing resistance, they help prevent excessive current that could damage components or create safety hazards.
2. **Dividing Voltages**: Resistors can also be used to create voltage dividers, which allow engineers to obtain a specific voltage from a higher voltage source. This is particularly useful in sensor applications where a specific voltage level is required for proper operation.
B. Types of Resistors
1. **Fixed Resistors**: These resistors have a constant resistance value and are commonly used in circuits to set specific current levels. They are available in various resistance values and power ratings, making them versatile for different applications.
2. **Variable Resistors**: Also known as potentiometers or rheostats, these allow users to adjust the resistance value. This adjustability makes them useful for applications like volume controls in audio equipment, where users can change the output level.
3. **Specialty Resistors**: These include thermistors, which change resistance with temperature, and photoresistors, which vary resistance based on light exposure. Specialty resistors are often used in specific applications, such as temperature sensing or light detection.
III. The Symbol of the Resistor
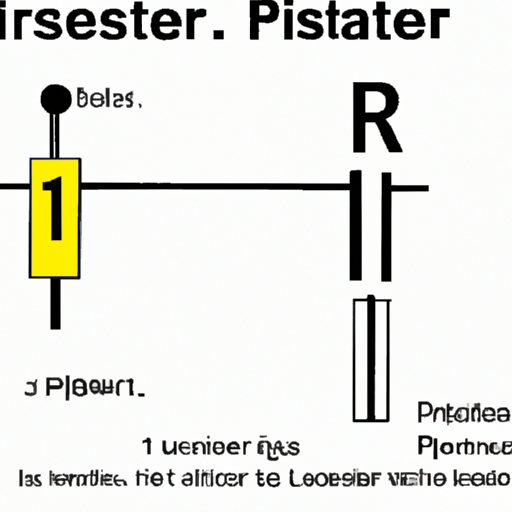
In circuit diagrams, the resistor is represented by a standardized symbol. The most common symbol consists of a zigzag line, which visually conveys the concept of resistance. This symbol is universally recognized and is used in various schematic representations.
A. Standard Symbol in Circuit Diagrams
1. **Description of the Symbol**: The zigzag line typically represents a fixed resistor. This design is simple yet effective, allowing anyone familiar with electrical schematics to quickly identify the component's function.
2. **Variations in Symbols**: Different types of resistors have distinct symbols. For instance, a potentiometer is represented with a zigzag line and an arrow, indicating the adjustable part. A rheostat may have a similar representation but with a different orientation, reflecting its specific use in circuits.
B. Historical Context of the Resistor Symbol
The development of electrical symbols, including that of the resistor, has evolved over time. The standardization of these symbols by organizations such as the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has facilitated clearer communication in the field of electrical engineering.
The need for standardized symbols arose as electrical engineering became more complex and widespread. Engineers and technicians from different regions and backgrounds needed a common language to communicate their designs effectively. The zigzag symbol for resistors, along with other standardized symbols, emerged as a solution to this challenge.
IV. Importance of the Resistor Symbol in Circuit Diagrams
The symbol of the resistor is not merely a representation; it plays a crucial role in the communication of ideas among engineers and technicians. Circuit diagrams serve as blueprints for electrical systems, and the clarity of these diagrams is paramount for effective design and analysis.
A. Role in Communication
The standardized symbol allows engineers from different backgrounds and regions to understand circuit designs without ambiguity. This is particularly important in collaborative projects where multiple engineers may contribute to a single design. The use of universally recognized symbols ensures that everyone involved can interpret the diagrams accurately.
B. Clarity in Circuit Design
A well-drawn circuit diagram with clear symbols, including that of the resistor, aids in troubleshooting and ensures that the circuit functions as intended. When engineers can quickly identify components and their functions, they can diagnose issues more efficiently and implement solutions effectively.
C. Examples of Circuit Diagrams
In various circuit diagrams, resistors are often used in conjunction with other components, such as capacitors and transistors, to create complex systems. The presence of the resistor symbol helps to delineate its role within the circuit. For example, in an audio amplifier circuit, resistors may be used to set gain levels, while in a power supply circuit, they may help regulate voltage levels.
V. Practical Applications of Resistors
Resistors are ubiquitous in electronic devices, serving a multitude of functions. They are found in everything from simple LED circuits to sophisticated audio amplifiers. Their ability to control current and voltage makes them indispensable in ensuring the proper functioning of electronic systems.
A. Use in Everyday Electronic Devices
Resistors are commonly used in devices like radios, televisions, and computers to manage current flow and protect sensitive components. For instance, in a simple LED circuit, a resistor is used to limit the current flowing through the LED, preventing it from burning out.
B. Role in Complex Circuits
In more intricate designs, resistors are used in filters, amplifiers, and oscillators, where precise control of electrical signals is necessary. For example, in an audio amplifier, resistors are used to set the gain and frequency response, ensuring that the output sound is clear and balanced.
C. Importance in Safety
Resistors also play a critical role in protecting components from excessive current, thereby preventing damage and ensuring the longevity of electronic devices. In power supply circuits, resistors can help dissipate excess energy, reducing the risk of overheating and failure.
VI. Conclusion
In summary, the symbol of the resistor is a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering that facilitates communication and understanding in circuit design. Its significance extends beyond mere representation; it embodies the principles of resistance that are crucial for the functionality of electronic systems. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of understanding electrical symbols, including that of the resistor, remains paramount for engineers and technicians alike.
Exploring these symbols further can enhance one’s knowledge and appreciation of the intricate world of electrical engineering. Whether you are a student, a hobbyist, or a professional engineer, familiarizing yourself with the symbols and their meanings will undoubtedly enrich your understanding of circuit design and analysis. As you continue your journey in electrical engineering, remember that each symbol tells a story about the components and their roles in the fascinating world of electronics.
What is the Symbol of the Resistor?

I. Introduction
In the realm of electrical engineering, resistors play a pivotal role in controlling the flow of electric current within circuits. These components are essential for a variety of applications, from simple household devices to complex electronic systems. Understanding the symbol of the resistor is crucial for anyone involved in circuit design or analysis, as it serves as a universal language among engineers and technicians. This article aims to delve into the symbol of the resistor, its historical context, and its significance in circuit diagrams.
II. Understanding Resistors
Resistors are passive electrical components that limit the flow of electric current in a circuit. Their primary function is to provide resistance, which can be used to control voltage and current levels. Resistors come in various types, each serving specific purposes:
A. Basic Function of Resistors
1. **Limiting Current Flow**: Resistors are primarily used to limit the amount of current that can flow through a circuit. By introducing resistance, they help prevent excessive current that could damage components or create safety hazards.
2. **Dividing Voltages**: Resistors can also be used to create voltage dividers, which allow engineers to obtain a specific voltage from a higher voltage source. This is particularly useful in sensor applications where a specific voltage level is required for proper operation.
B. Types of Resistors
1. **Fixed Resistors**: These resistors have a constant resistance value and are commonly used in circuits to set specific current levels. They are available in various resistance values and power ratings, making them versatile for different applications.
2. **Variable Resistors**: Also known as potentiometers or rheostats, these allow users to adjust the resistance value. This adjustability makes them useful for applications like volume controls in audio equipment, where users can change the output level.
3. **Specialty Resistors**: These include thermistors, which change resistance with temperature, and photoresistors, which vary resistance based on light exposure. Specialty resistors are often used in specific applications, such as temperature sensing or light detection.
III. The Symbol of the Resistor
In circuit diagrams, the resistor is represented by a standardized symbol. The most common symbol consists of a zigzag line, which visually conveys the concept of resistance. This symbol is universally recognized and is used in various schematic representations.
A. Standard Symbol in Circuit Diagrams
1. **Description of the Symbol**: The zigzag line typically represents a fixed resistor. This design is simple yet effective, allowing anyone familiar with electrical schematics to quickly identify the component's function.
2. **Variations in Symbols**: Different types of resistors have distinct symbols. For instance, a potentiometer is represented with a zigzag line and an arrow, indicating the adjustable part. A rheostat may have a similar representation but with a different orientation, reflecting its specific use in circuits.
B. Historical Context of the Resistor Symbol
The development of electrical symbols, including that of the resistor, has evolved over time. The standardization of these symbols by organizations such as the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has facilitated clearer communication in the field of electrical engineering.
The need for standardized symbols arose as electrical engineering became more complex and widespread. Engineers and technicians from different regions and backgrounds needed a common language to communicate their designs effectively. The zigzag symbol for resistors, along with other standardized symbols, emerged as a solution to this challenge.
IV. Importance of the Resistor Symbol in Circuit Diagrams
The symbol of the resistor is not merely a representation; it plays a crucial role in the communication of ideas among engineers and technicians. Circuit diagrams serve as blueprints for electrical systems, and the clarity of these diagrams is paramount for effective design and analysis.
A. Role in Communication
The standardized symbol allows engineers from different backgrounds and regions to understand circuit designs without ambiguity. This is particularly important in collaborative projects where multiple engineers may contribute to a single design. The use of universally recognized symbols ensures that everyone involved can interpret the diagrams accurately.
B. Clarity in Circuit Design
A well-drawn circuit diagram with clear symbols, including that of the resistor, aids in troubleshooting and ensures that the circuit functions as intended. When engineers can quickly identify components and their functions, they can diagnose issues more efficiently and implement solutions effectively.
C. Examples of Circuit Diagrams
In various circuit diagrams, resistors are often used in conjunction with other components, such as capacitors and transistors, to create complex systems. The presence of the resistor symbol helps to delineate its role within the circuit. For example, in an audio amplifier circuit, resistors may be used to set gain levels, while in a power supply circuit, they may help regulate voltage levels.
V. Practical Applications of Resistors
Resistors are ubiquitous in electronic devices, serving a multitude of functions. They are found in everything from simple LED circuits to sophisticated audio amplifiers. Their ability to control current and voltage makes them indispensable in ensuring the proper functioning of electronic systems.
A. Use in Everyday Electronic Devices
Resistors are commonly used in devices like radios, televisions, and computers to manage current flow and protect sensitive components. For instance, in a simple LED circuit, a resistor is used to limit the current flowing through the LED, preventing it from burning out.
B. Role in Complex Circuits
In more intricate designs, resistors are used in filters, amplifiers, and oscillators, where precise control of electrical signals is necessary. For example, in an audio amplifier, resistors are used to set the gain and frequency response, ensuring that the output sound is clear and balanced.
C. Importance in Safety
Resistors also play a critical role in protecting components from excessive current, thereby preventing damage and ensuring the longevity of electronic devices. In power supply circuits, resistors can help dissipate excess energy, reducing the risk of overheating and failure.
VI. Conclusion
In summary, the symbol of the resistor is a fundamental aspect of electrical engineering that facilitates communication and understanding in circuit design. Its significance extends beyond mere representation; it embodies the principles of resistance that are crucial for the functionality of electronic systems. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of understanding electrical symbols, including that of the resistor, remains paramount for engineers and technicians alike.
Exploring these symbols further can enhance one’s knowledge and appreciation of the intricate world of electrical engineering. Whether you are a student, a hobbyist, or a professional engineer, familiarizing yourself with the symbols and their meanings will undoubtedly enrich your understanding of circuit design and analysis. As you continue your journey in electrical engineering, remember that each symbol tells a story about the components and their roles in the fascinating world of electronics.










